



PhD student of Economic Development Policy and Management Program
About me
I am a PhD student from the Graduate School of International Development at Nagoya University in Japan. My research interest focuses on regional economics and industrial structure, combined with spatial data analysis, remote sensing data analysis, machine learning, and causal inference. My current research deals with: (1). regional inequality and convergence; (2). economic growth and geospatial heterogeneity; (3). structural change and regional income dynamics.
You can download my CV here.
Interests:
- Regional inequality
- Structural change
- Spatial Econometrics
- Remote Sensing Data Analysis
Education:
- PhD student in Development Economics, 2022-now
Nagoya University, JAPAN
- MSc in Marketing, 2020
University of Manchester, UK
- BA in Japanese Economics and Trade, 2019
Donghua University, CHINA
My publications
Yilin Chen, Ursavas Ugur, Carlos Mendez
April 2024 . Letters in Spatial and Resource Sciences


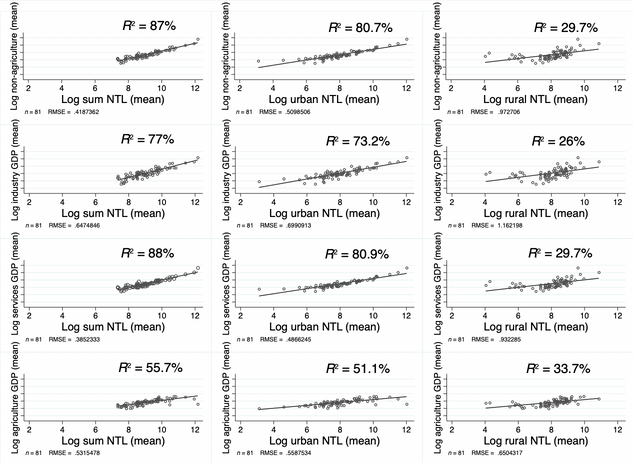
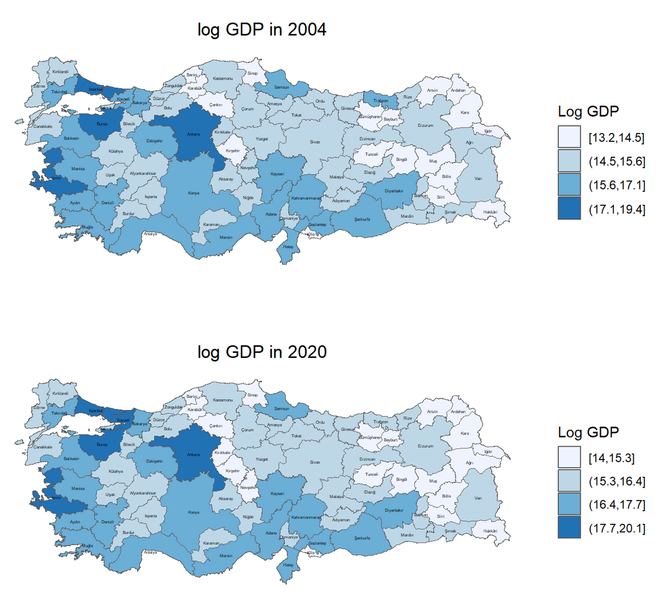

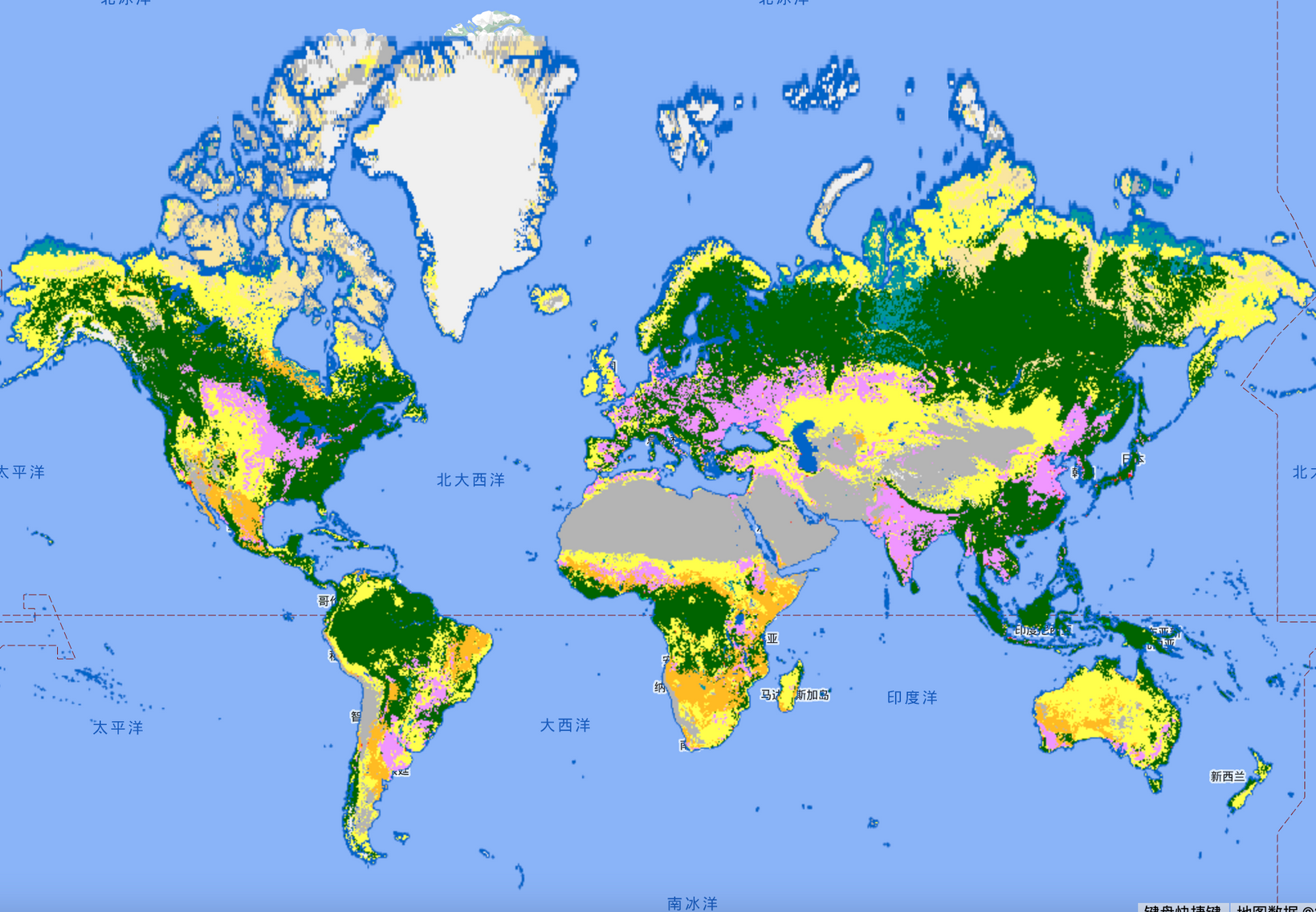
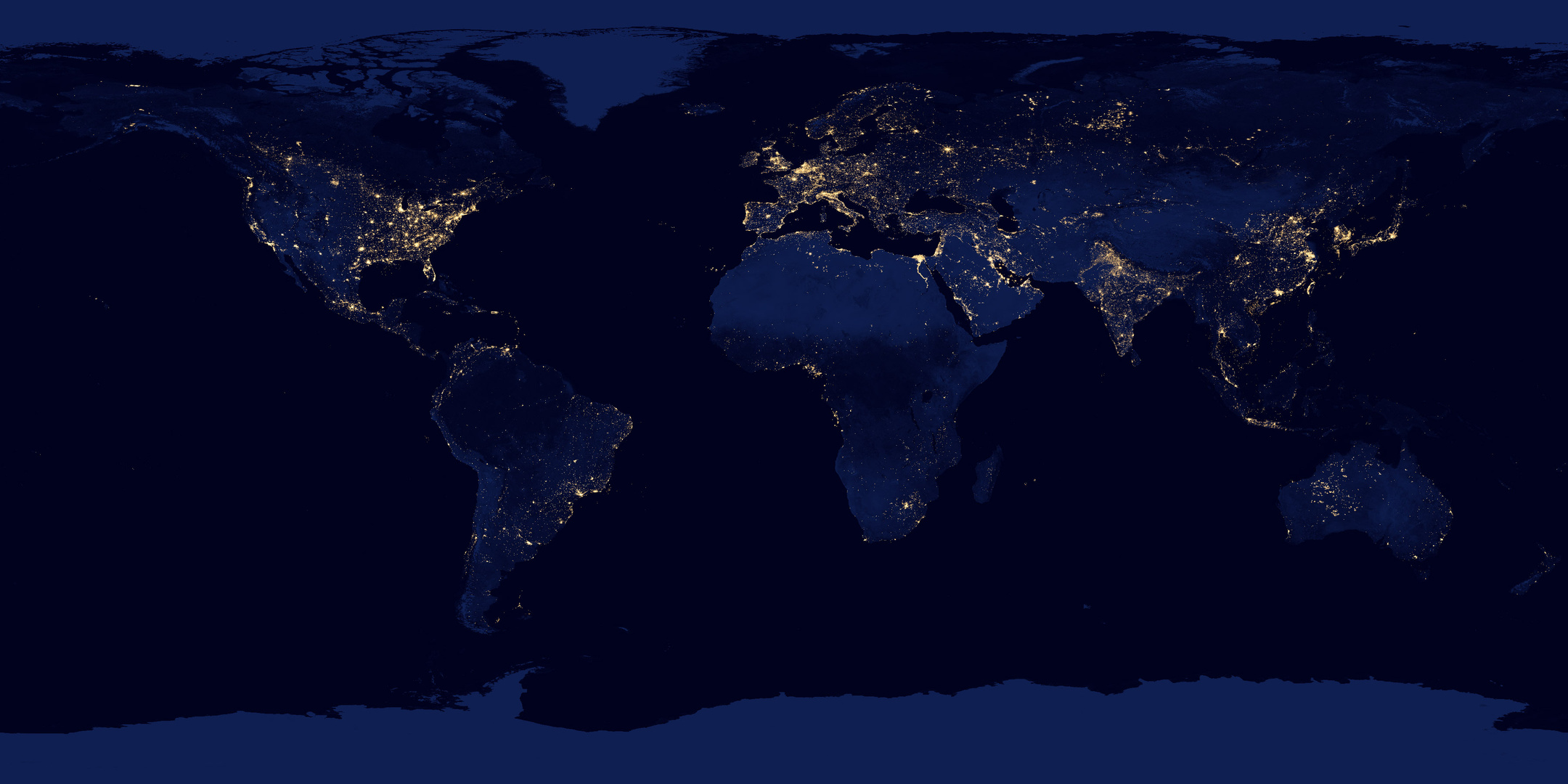
This study investigates the potential of higher-quality nighttime light (NTL) to predict the sub-national sectoral GDP in Türkiye.

Yilin Chen
February 2024 . Asia-Pacific Journal of Regional Science

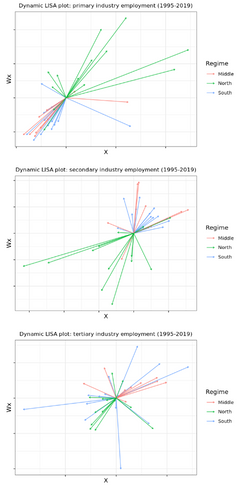

This study explores the spatio-temporal pattern of regional income and industrial structure across resource cities in northeast China.
PDF

April 2024
Yilin Chen, Dohèto Othniel Kpoviessi, Harry Aginta
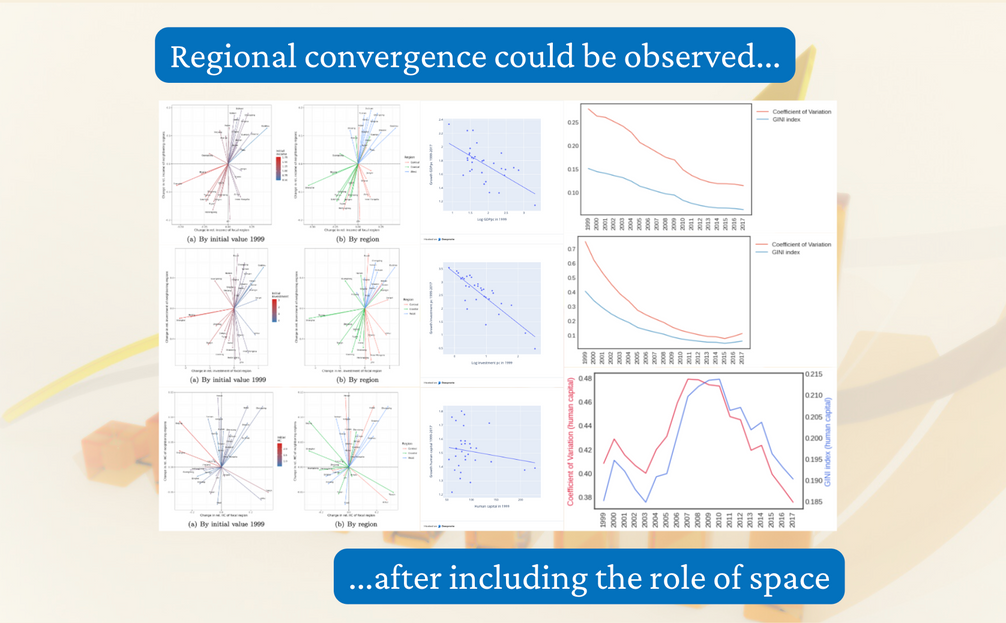
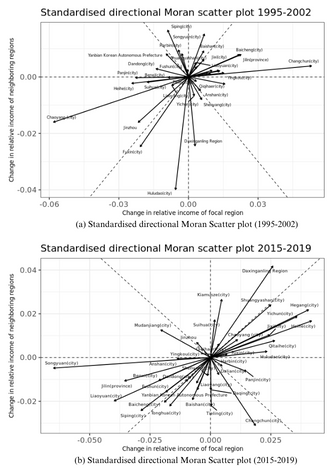
This study explores the space-time pattern and the regional convergence for several economic indicators across Chinese provinces.
PDF
Spatial evolution of (1) GDP; (2) investment; (3) human capital index
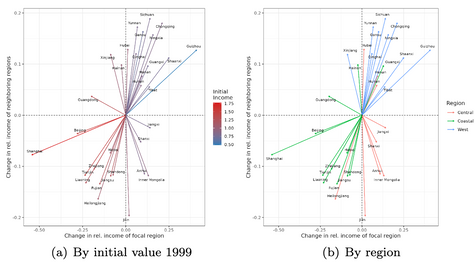
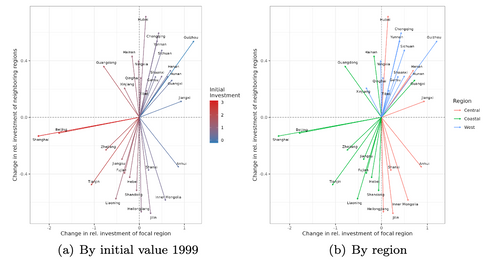
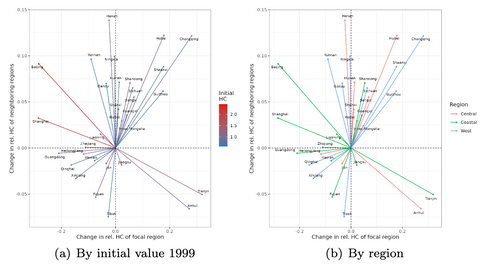
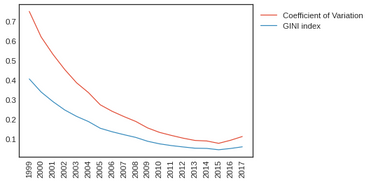
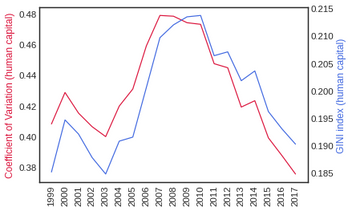
Beta convergence of (a) GDP; (b) investment; (c) human capital index
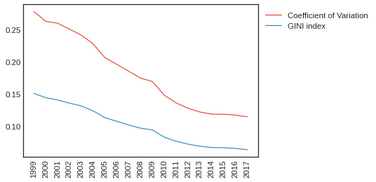
Sigma convergence of (a) GDP; (b) investment; (c) human capital index
Type Jounal Article
Publication Letters in Spatial and Resource Sciences
Abstract
Uneven regional development has become an issue in China since the Open and Reform Policy in the 1980s. The imbalance can be observed as the “coastal-west divide” in previous convergence studies. This paper aims to investigate the convergence of income and its determinants across Chinese provinces from 1999 to 2017 by including the role of space. Our findings from a new exploratory technique in spatial analysis show convergence in income and investment but not in human capital, which is in line with results from non-spatial classical convergence models. We confirm the investment-driven economy in China and suggest that investment mainly facilitates the convergence trend of regional income and gradually narrows the coastal-wide divide. Targeting investment and spatial connectivity in low-income regions could be a key policy direction to achieve balanced regional development.
Keywords: Income convergence . ESTDA . China . Investment . Human capital
Type Jounal Article
Publication Asia-Pacific Journal of Regional Science
Abstract
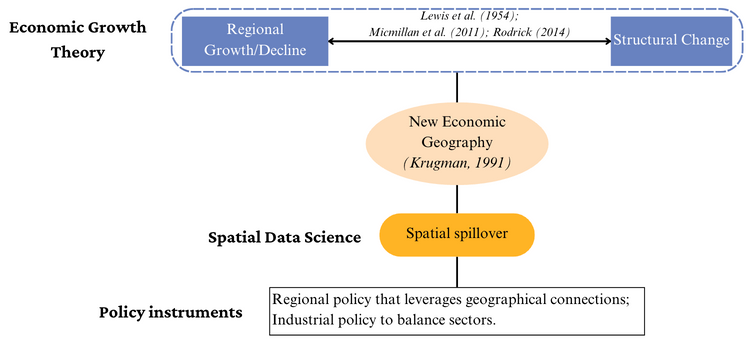
Literature on New Economic Geography (NEG) highlights the importance of spatial concentration and spillover effects in economic growth or decline. Northeast China, as an old industrial base, is experiencing a regional decline since its transition to the post-industrial stage. Therefore, what is the main sectoral composition in Northeast China and how does this influence regional decline? To what extent do spatial spillovers play a role before and during the regional decline of Northeast China? Based on these questions, we investigated the spatial connections between regional decline and structural changes in Northeast China over three development periods: Rust Belt (1995–2002), revival (2002–2015), and decline (2015–2019). The recent exploratory space–time data analysis was employed on prefecture-level income and its structural change components (sectoral output and employment ratio). We found that the possible reason for the regional decline in Northeast China is premature deindustrialisation. Spatial co-decline in the employment of industry and construction, the primary source of regional decline, facilitates most of the space–time patterns of the regional income. Agglomeration of the agricultural sector has shifted to the north, while industry and construction have gravitated towards the middle and south, with no clear spatial patterns in the service sector. Dependence on natural resources has a "lock-in effect" that inhibits the transition from industry to services, so industry and construction remain the most efficient in Northeast China. Strengthening spatial connections is essential for local governments to develop service sectors and overcome declining conditions.
Keywords: Regional decline . Structural change . ESTDA (exploratory space–time data analysis) . Resource dependence . Northeast China
Type Jounal Article
Publication Letters in Spatial and Resource Sciences
Abstract
Limited access to regional and sectoral economic data hinders effective policy design in various countries. To address this issue, this study explores the potential of higherquality nighttime light (NTL) data to predict economic activity across various sectors within regions. We analyze the relationship between NTL intensity and sectoral GDP in 81 Turkish provinces from 2004 to 2020. Our findings reveal that urban NTL data is most strongly correlated with non-agricultural GDP, particularly in the industrial sector. This suggests that NTL data, especially its urban component, can be a valuable tool for policymakers to identify economically disadvantaged regions and sectors, monitor the impact of economic development policies at a granular level, and allocate resources efficiently. However, this study also acknowledges limitations in capturing annual GDP changes, highlighting the need to combine NTL data with other economic indicators for a comprehensive understanding.
Keywords: Satellite imagery · Nighttime lights · Sectoral GDP · Türkiye

My Research Results
Time series lines of city level GDP in Northeast China
Average provincial production and employment ratio

My working progress
- Nighttime Lights and Economic Activity: Evidence from Developed and Developing Countries, joint work with Carlos Mendez and Hussein Suleiman, manuscript submitted;
- Remotely sensed spatial inequality: Luminosity evidence from Chinese cities and counties, single author, manuscript submitted.
- Regional Inequality and Spatial Structural Change in China: A Remote Sensing Approach “Day and Night”, single author, working in progress.
- Heterogenous impact of structural change on regional inequality in China, single author, working in progress.
Contact
chen.yilin.r4@s.mail.nagoya-u.ac.jp
Furocho, Chikusa-ku, Nagoya, Aichi, JAPAN 464-8601







